Caution: Using the Ntdsutil utility incorrectly may result in partial or complete loss of Active Directory functionality.
To clean up metadata
Note: Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 eliminates the need for the above step.

At this point, Active Directory confirms that the domain controller
was removed successfully. If you receive an error that the object could
not be found, Active Directory might have already removed from the
domain controller.
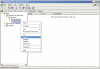
To remove the failed server object from the domain controllers container
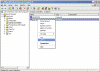

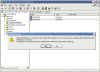
To remove the failed server object from DNS
Also, consider the following:
To clean up metadata
- At the command line, type Ntdsutil and press ENTER.
- At the Ntdsutil: prompt, type metadata cleanup and press Enter.
- At the metadata cleanup: prompt, type connections and press Enter.
- At the server connections: prompt, type connect to server <servername>, where <servername> is the domain controller (any functional domain controller in the same domain) from which you plan to clean up the metadata of the failed domain controller. Press Enter.
- Type quit and press Enter to return you to the metadata cleanup: prompt.
- Type select operation target and press Enter.
- Type list domains and press Enter. This lists all domains in the forest with a number associated with each.
- Type select domain <number>, where <number> is the number corresponding to the domain in which the failed server was located. Press Enter.
- Type list sites and press Enter.
- Type select site <number>, where <number> refers to the number of the site in which the domain controller was a member. Press Enter.
- Type list servers in site and press Enter. This will list all servers in that site with a corresponding number.
- Type select server <number> and press Enter, where <number> refers to the domain controller to be removed.
- Type quit and press Enter. The Metadata cleanup menu is displayed.
- Type remove selected server and press Enter.
Sponsored
- Type quit, and press Enter until you return to the command prompt.
- In Active Directory Sites and Services, expand the appropriate site.
- Delete the server object associated with the failed domain controller.

To remove the failed server object from the domain controllers container
- In Active Directory Users and Computers, expand the domain controllers container.
- Delete the computer object associated with the failed domain controller.

- Windows Server 2003 AD might display a new type of question window, asking you if you want to delete the server object without performing a DCPROMO operation (which, of course, you cannot perform, otherwise you wouldn’t be reading this article, would you…) Select “This DC is permanently offline…” and click on the Delete button.

- AD will display another confirmation window. If you’re sure that you want to delete the failed object, click Yes.

To remove the failed server object from DNS
- In the DNS snap-in, expand the zone that is related to the domain from where the server has been removed.
- Remove the CNAME record in the _msdcs.root domain of forest zone in DNS. You should also delete the HOSTNAME and other DNS records.

- If you have reverse lookup zones, also remove the server from these zones.
Also, consider the following:
- If the removed domain controller was a global catalog server, evaluate whether application servers that pointed to the offline global catalog server must be pointed to a live global catalog server.
- If the removed DC was a global catalog server, evaluate whether an additional global catalog must be promoted to the address site, the domain, or the forest global catalog load.
- If the removed DC was a Flexible Single Master Operation (FSMO) role holder, relocate those roles to a live DC.
- If the removed DC was a DNS server, update the DNS client configuration on all member workstations, member servers, and other DCs that might have used this DNS server for name resolution. If it is required, modify the DHCP scope to reflect the removal of the DNS server.
- If the removed DC was a DNS server, update the Forwarder settings and the Delegation settings on any other DNS servers that might have pointed to the removed DC for name r